In a time when celebrity culture is more prevalent than ever due to social media, a recent study reveals a connection between adoring celebrities and underlying social and psychological factors. New findings indicate that insecure individuals with social anxiety are more likely to idolize public figures.
The psychology of idolizing celebrities
The internet has made it easier for people to form one-sided emotional connections with celebrities, also known as parasocial relationships. This is especially common among today’s young people, who increasingly idolize public figures. These relationships range from a simple interest in a celebrity’s well-being to an unhealthy obsession.
Previous research suggests that although interest in celebrities decreases from junior high through college, almost half of college students still have a favorite celebrity. Recent studies link celebrity adoration to behavioral addictions, such as gambling,
excessive use of the internet substance abuse, dependence on social media, and . Additionally, intense celebrity adoration is associated with negative psychological effects like anxiety, depression, and obsessive thoughts.Psychologists at Shaanxi Normal University aimed to validate the absorption-addiction model, which suggests that people who hold celebrities in almost cult-like reverence do so to fill personal and social voids. The researchers surveyed 1,147 young adults from various universities in China.
The participants were evaluated for four main factors:
celebrity worship, which measures the level of personal devotion to a favorite celebrity across different dimensions, from purely entertainment purposes to borderline-pathological obsession.
- social anxiety, focusing on the participants’ experience of anxiety in social situations over the past week.
- reliance on mobile phones, assessed using a specific scale that explores addictive symptoms across various aspects, such as inability to control craving and feeling anxious and lost without the device.
- socioeconomic status, estimated based on parental income levels.
- From admiration to obsession
Theoretical model of relationships between social anxiety, celebrity worship and mobile phone dependence. Credit: BMC Psychology.
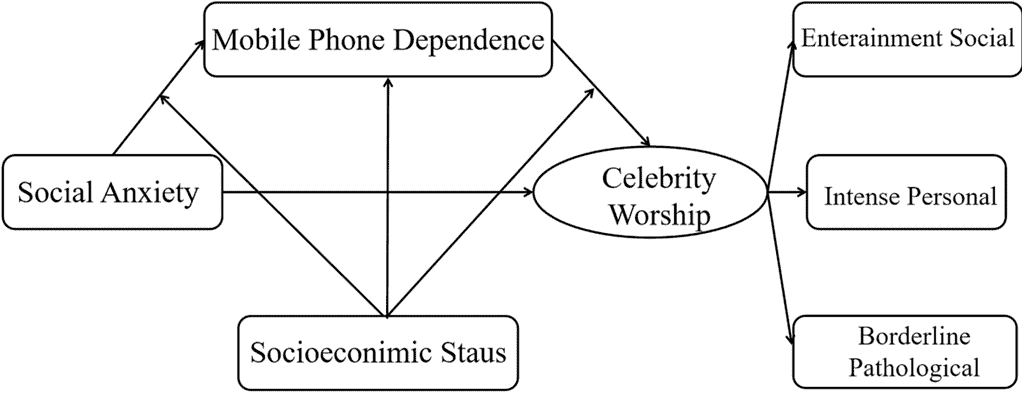
The study confirms that social anxiety significantly predicts celebrity worship. This finding supports the theory that individuals may turn to celebrities to compensate for insufficient interpersonal relationships or a lack of meaningful social interactions. People with high levels of social anxiety are likely to use mobile phones more frequently as a coping mechanism, which, in turn, increases their engagement with celebrity culture. This
confirms previous studies that found social anxiety and excessive phone screen time are closely linked. Socioeconomic status (SES) was also positively linked to celebrity worship. Wealthier young individuals are able to donate money, purchase merchandise, or subscribe to paid services from their favorite celebrities.
At the same time, SES also plays a role. People from higher SES backgrounds have lower levels of phone dependence when dealing with social anxiety, indicating that SES can protect against excessive involvement in celebrity culture. The study also shows that women are generally more interested in celebrity adoration.
“Studies have shown that high SES parents are more involved and positive, which can enhance young people’s cognitive abilities and help them develop good habits, thus decreasing phone dependence,” the researchers stated.
This study focused on a specific group in China. It’s important to approach the findings with caution. Nevertheless, celebrity adoration is a real phenomenon that can sometimes become clinically extreme.
In a 2014 study called
“I’m Your Number One Fan — A Clinical Look at Celebrity Worship,” , researchers discovered that this type of one-sided relationship can lead to concerns about body image (especially among young teenagers), a higher likelihood of cosmetic surgery, sensation-seeking, cognitive inflexibility, identity confusion, and poor personal boundaries.It’s fine to admire a celebrity as long as it remains a healthy source of inspiration, rather than turning into an obsession.
The new findings were published in the journal
BMC Psychology. Was this useful?.









