For the first time in human history we have witnessed a black hole in the act of ‘eating’ a star that just got too close. So far, astronomers have only found the aftermath of such events, and they say that seeing the black hole in the act is shedding a lot of light on ‘relativistic jets‘.

It all started when the Swift satellite observed a string of extremely bright bursts of gamma rays from outside our galaxy; nothing extremely unusual here, scientists have observed gamma ray bursts in the past, but their patters was unlike anything they’d ever seen before.
“It was nothing like we expected for a gamma-ray burst,” said Ashley Zauderer, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics who co-authored a different study on the event.
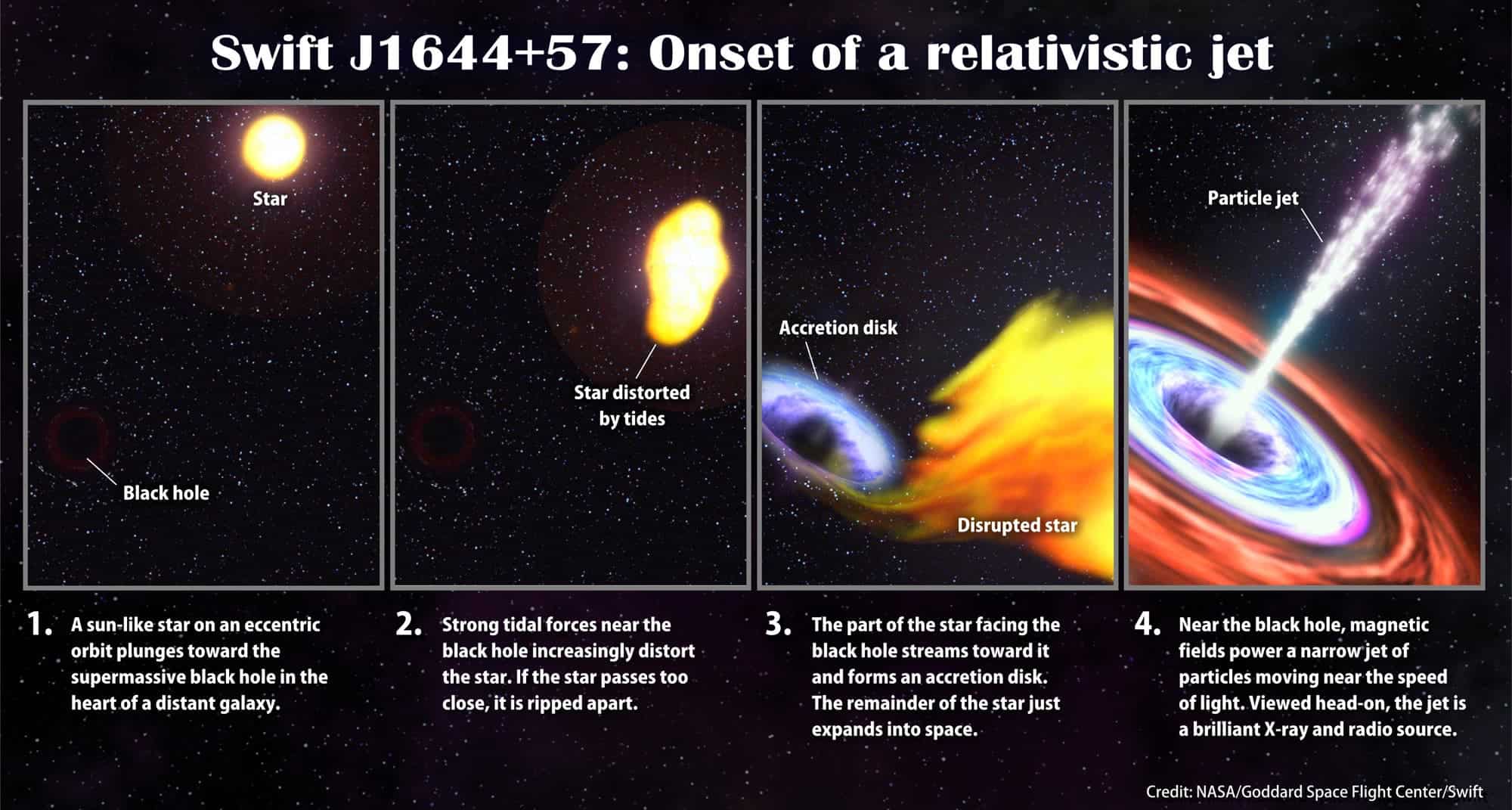
Additional observations revealed that the flare occured at a supermassive black hole from the center of a galaxy, and the source of this radiation was expanding at 99.5 the speed of light. Based on this data, researchers estimated that the black hole in case is about 1.000.000 times heavier than the Sun, which makes it similar to the one from the center of the Milky Way. The event is not earthshattering, but it does deal with a phenomena that wasn’t discussed before.
There are a lot more surprises in space for us to discover, especially as we continue to make huge strides in the technical capabilities of our instruments,” Zauderer said.









