Humans, as well as most mammals, have only two sets of teeth to make with during their entire lifetime. However, a new research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, which studied the dental structure of mole rats has shown that the species is an exception to this rule. In fact, they’re very much similar to sharks, which grow a new set of teeth regularly and change them like a conveyor belt.
In 1957, Stuart Landry first observed that the mole rat had more molars than the average rodent, however this particular fact never interested anyone enough to study the matter further – until now that is, after Helder Gomes Rodrigues from the University of Lyon made this remarkable discovery.
Apart from the mole rat, there are only four other mammals capable of changing their teeth regularly, namely three different manatee species and a pygmy-rock wallaby. Still, the mole rat is unique among mammals, in terms that it has a peculiar up and down movement of its teeth with concomitant rows of teeth sprouting. The other multiple tooth generating mammals first loose their old teeth and then grow a new set, similar to how regular mammals grow a new set after they lose their baby teeth.
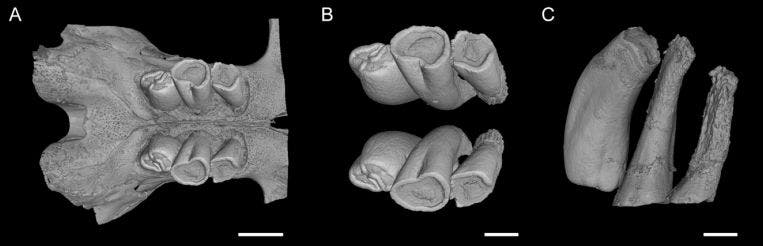
For his research, Rodrigues analyzed 55 specimens and observed that in each one the back molars in the jaw of the rodents move forward, this although the old one hadn’t come out yet. The researchers saw that by the time the new molars finally reached the first ray, they displayed a very eroded structure from all the wear and tear.
The scientists then sought to find an explanation to this peculiar exception. The manatees and pygmy-rock wallaby have earned the ability to replace their teeth due to the hard elements in their die, however this is not the case with your typical soft plants eating mole rat. Instead, a viable evolutionary explination the researchers have come up with is that their unique ability is due to the fact they primarily dig with their front incisors, they grind things with their molars and swallow abrasive dust.
source