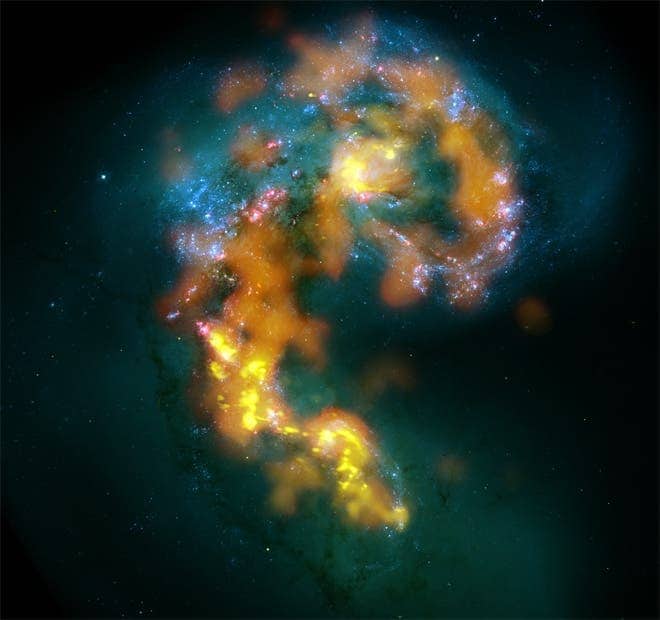A new radio telescope array built in the world’s highest and driest desert in the world has just photographed two colliding galaxies for its first public test shots.
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, a joint project between Canada, Chile, the European Union, Japan, Taiwan and the United States was officially opened for business after a decade of planning and building. The world’s largest astronomy project, ALMA is described as the most powerful millimeter/submillimeter-wavelength telescope ever and the most complex ground-based observatory, and these first images are a perfect description of what it has to give.
Today marks the recognition of the successful coalition of thousands of people from all over the world all working with the same goal: to build the world’s most advanced radio telescope to see into the universe’s coldest, darkest places, where galaxies and stars and perhaps the building blocks of life are created,” said ALMA director Thijs de Graauw.

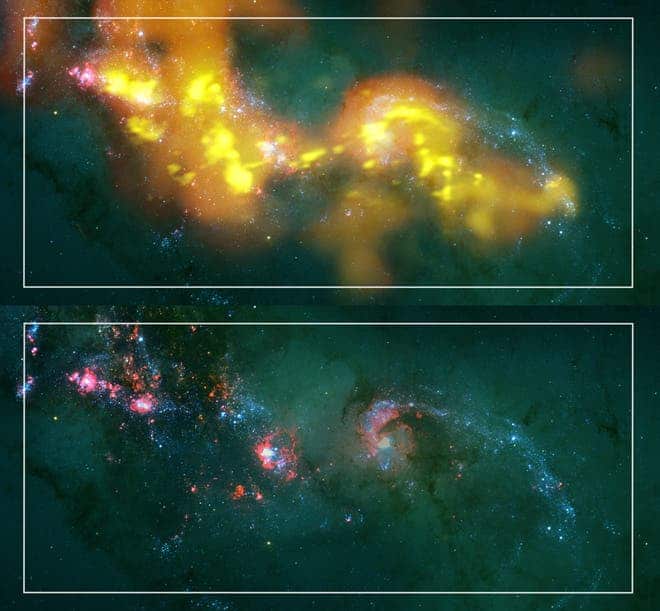
What ALMA photographed isn’t visible in normal light, because the murky material that leads to star birth blocks visible wavelengths of light.
“In the past we couldn’t study them because they were behind the dust. The thing that’s been missing is the youngest stars, which are the most interesting,” said astronomer Brad Whitmore of the Space Telescope Science Institute in a webcast. “This is a beautiful example where we’ll be able to see the full life histories of star clusters.”
What happens is that gas and dust absorb the light of stars and then re-emit the energy, but in different wavelengths of light. However, like black out curtains the thickest molecular dust clouds trap almost all wavelengths, making them extremely hard to spot.
Radio waves are an exception; in the same way that radio frequencies pass even through the thickest of walls, so do they pass through these dust clouds; and ALMA is capable of not only noticing the presence of hot young stars, but also determine rich chemical information about them.
“For the last 25 years, we have really only relied on being able to see carbon monoxide or hydrogen cyanide,” said astronomer Kartik Sheth of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory in the webcast. “For the first time, we can see the entire chemical spectrum.”

“We will use ALMA to image the ‘birth ring’ of planetesimals that we believe orbits this young star,” he said. “We hope to discover clumps in these dusty asteroid belts, which can be the markers of unseen planets.”
Via Wired