In a recent groundbreaking research study, scientists from Seoul National University in South Korea have successfully created a dog that can glow in the dark, using genetic engineering techniques. This achievement holds the potential for finding cures for human diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
The dog in question, a genetically modified female beagle named Tegon, was born in 2009 through a cloning technique. By inserting genes that cause human illnesses into dogs and controlling their activation, researchers can study these diseases and develop potential cures.
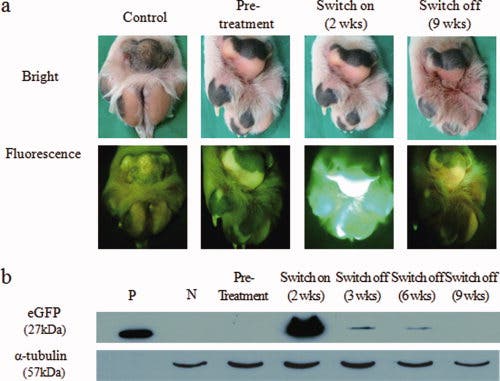
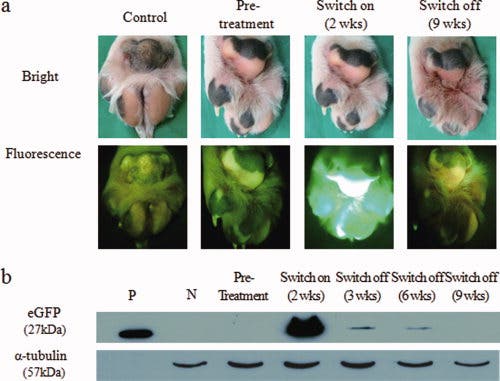
The remarkable ability of Tegon to glow in the dark was made possible by adding enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) to the nucleus of a cell, which was then placed inside an egg. The researchers conducted a two-year test and found that the dog’s ability to glow can be controlled by administering a drug called doxycycline through its food.
Lead researcher Lee Byeong-chun stated, “The creation of Tegon opens new horizons since the gene injected to make the dog glow can be substituted with genes that trigger fatal human diseases.”
The same technology, called somatic cell nuclear transfer, was previously used to clone Snoopy, the first dog clone, in 2005 at the same university. Two years ago, the scientists also created Ruby Puppy, or Ruppy, a dog that glows red fluorescent.
For more detailed information on this $3 million study, you can refer to the article published in the Journal of Genetics.