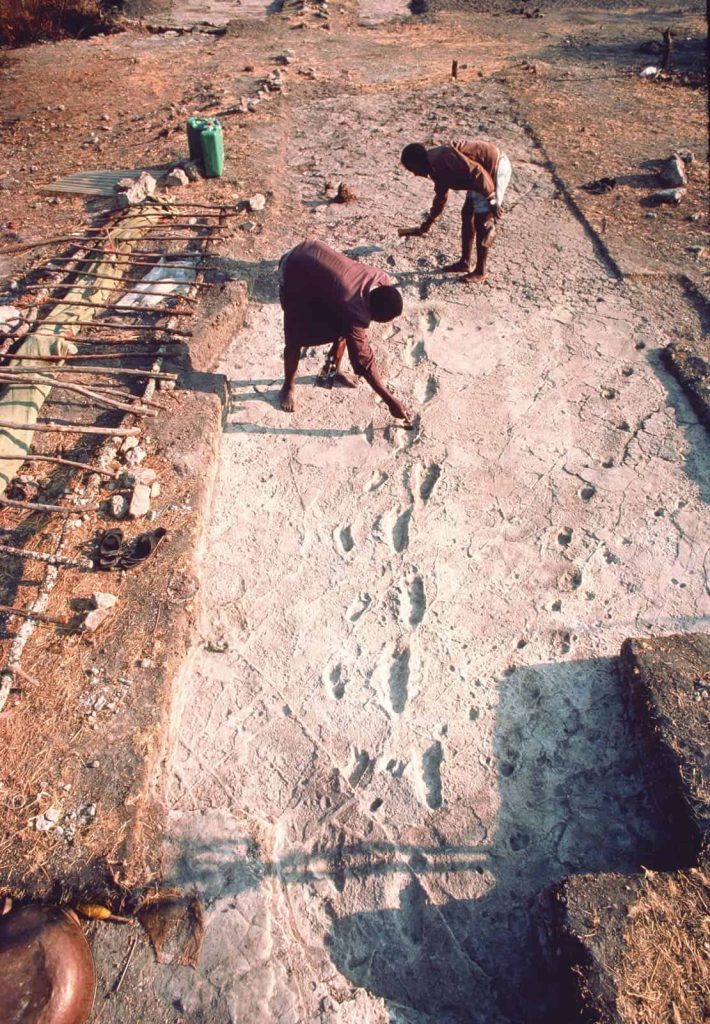
Researchers from the University of Liverpool have found ancient footprints in Laetoli, Tanzania, suggesting the fact that human-like features of the feet and gait existed a couple of million years earlier than previously believed.
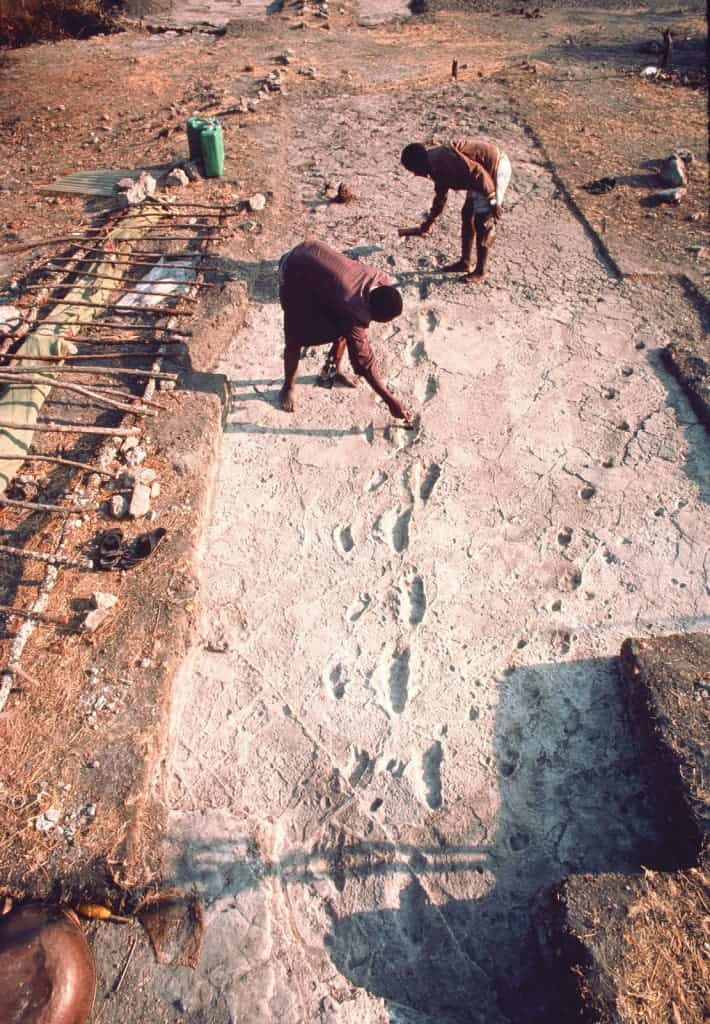

Professor Robin Crompton, from the University of Liverpool’s Institute of Ageing and Chronic Disease, said: “It was previously thought that Australopithecus afarensis walked in a crouched posture, and on the side of the foot, pushing off the ground with the middle part of the foot, as today’s great apes do.
“We found, however, that the Laetoli prints represented a type of bipedal walking that was fully upright and driven by the front of the foot, particularly the big toe, much like humans today, and quite different to bipedal walking of chimpanzees and other apes. Quite remarkably, we found that some healthy humans produce footprints that are more like those of other apes than the Laetoli prints. The foot function represented by the prints is therefore most likely to be similar to patterns seen in modern-humans. This is important because the development of the features of human foot function helped our ancestors to expand further out of Africa.”