A recently published remarkable study describes how scientists from Japan have successfully manage to grow teeth inside a lab using mice stem cells.
Takashi Tsuji from Tokyo University of Science and his team managed to achieve this after extracting stem cells from the molars of mice. They then transported these cells to the lab where they eventually used them to grow new mouse teeth, which in order to have the required form had to be placed inside a mold. The new, lab-grown teeth were then transplanted in the jaws of mice – full attachment occurred within 40 days.
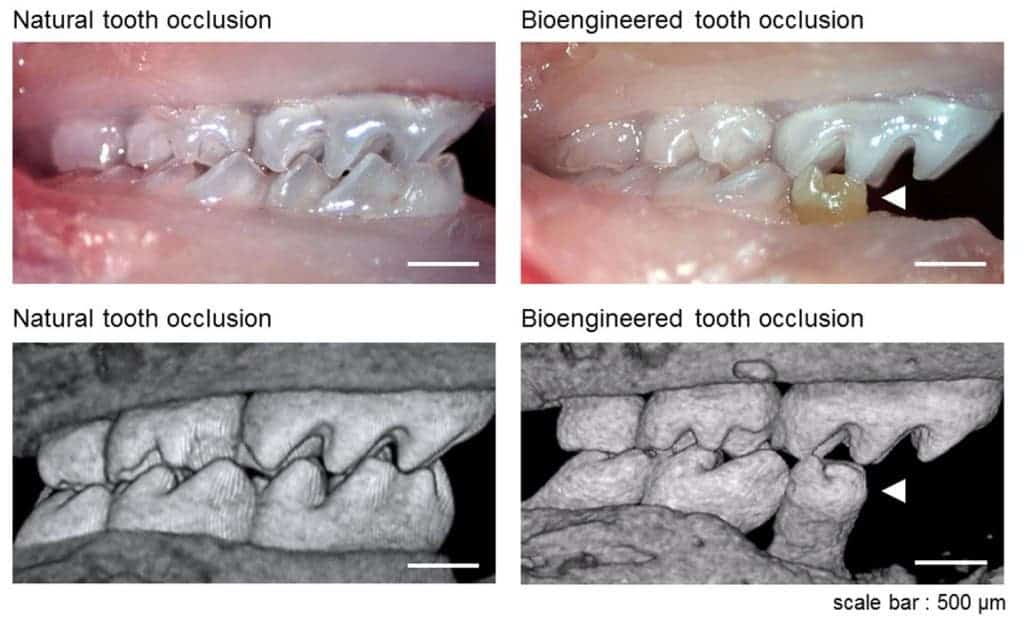
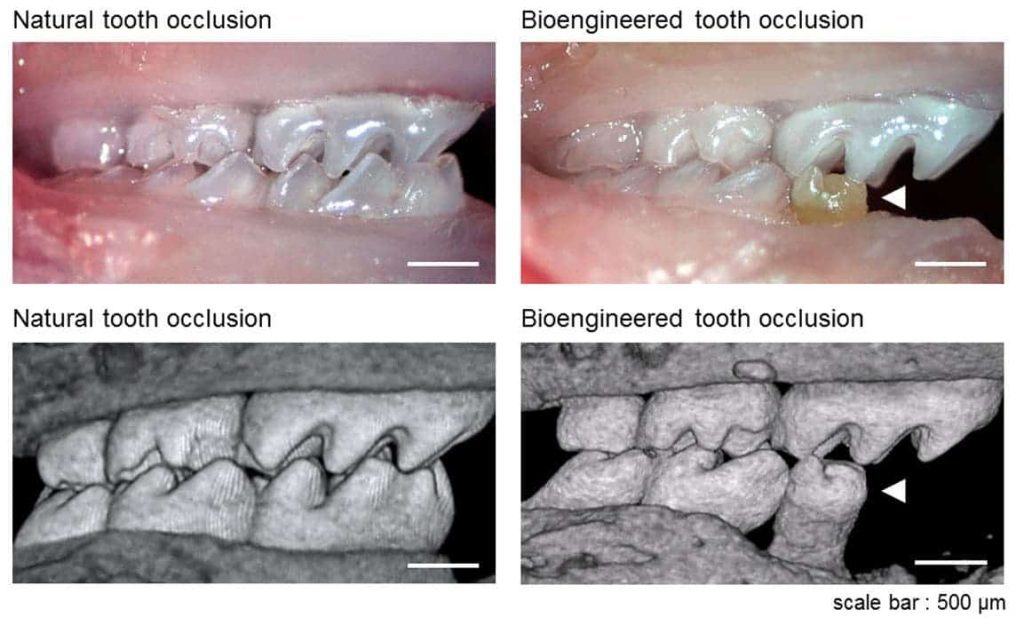
The transplanted teeth fixed themselves perfectly into the bone and tissue of the jaw, and researchers notice absolutely no evidence of chewing or eating discomforts from behalf of the mice. Remarkably enough, they also saw that nerve fibers had begun growing in the engineered teeth which makes for an almost perfect transplant.
Tsuji stresses that in order for reconstruction therapy to be successful, it is important to find the right seed cells. As was their case, they needed cells taken directly from the mice molars, complete with enamel and dental bones, in order to fully replicate them. Human transplants might become the standard in commercial dental repair in the next decades.
This is just one of the numerous recent advances from the field of stem cell research, and scientists hope that each piece they play might one day lead to a collective effort of finally stem cell engineering a human organ. The consequences of such an achievement would sound long and profound, and for ever change the face of surgical transplants and even longevity itself. Imagine, replacing your organs periodically whenever they start failing.
The paper was published in the open access journal PLoS One.