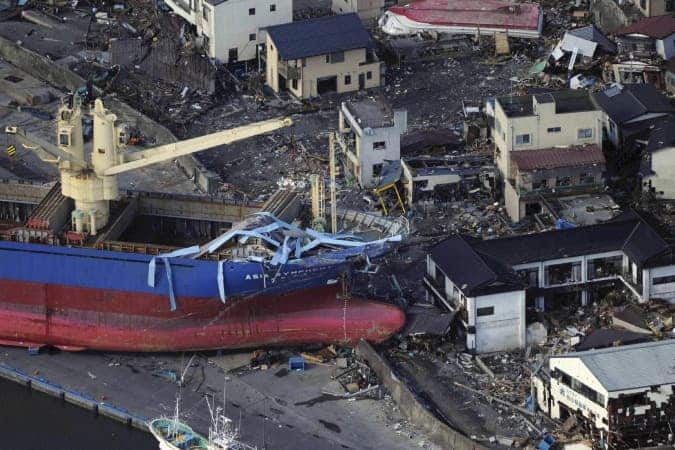
It’s no mystery for anybody that the earthquake in Japan is one of the largest ever to be recorded in history, and it’s no mystery for anybody that Japan is an area with numerous seismic events, but the magnitude of this one exceeded greatly all expectations, even the most pessimistic one.
The 8.9 magnitude (or 9.0 according to other measurements) earthquake that struck the northeastern coast of Japan “is going to be among the top 10 earthquakes recorded since we have had seismographs,” said seismologist Susan Hough of the U.S. Geological Survey in Pasadena. “It’s bigger than any known historic earthquake in Japan, and bigger than expectations for that area.”
That particular portion of the Ring of Fire, as it is called, was expected to create a 8, maybe 8.5 magnitude temblor, but something as big as 8.9 is quite surprising; this may not seem like a big difference, but the Richter scale is a logarithmic one, so a 9 earthquake is 10 times more powerful than a 8 earthquake.
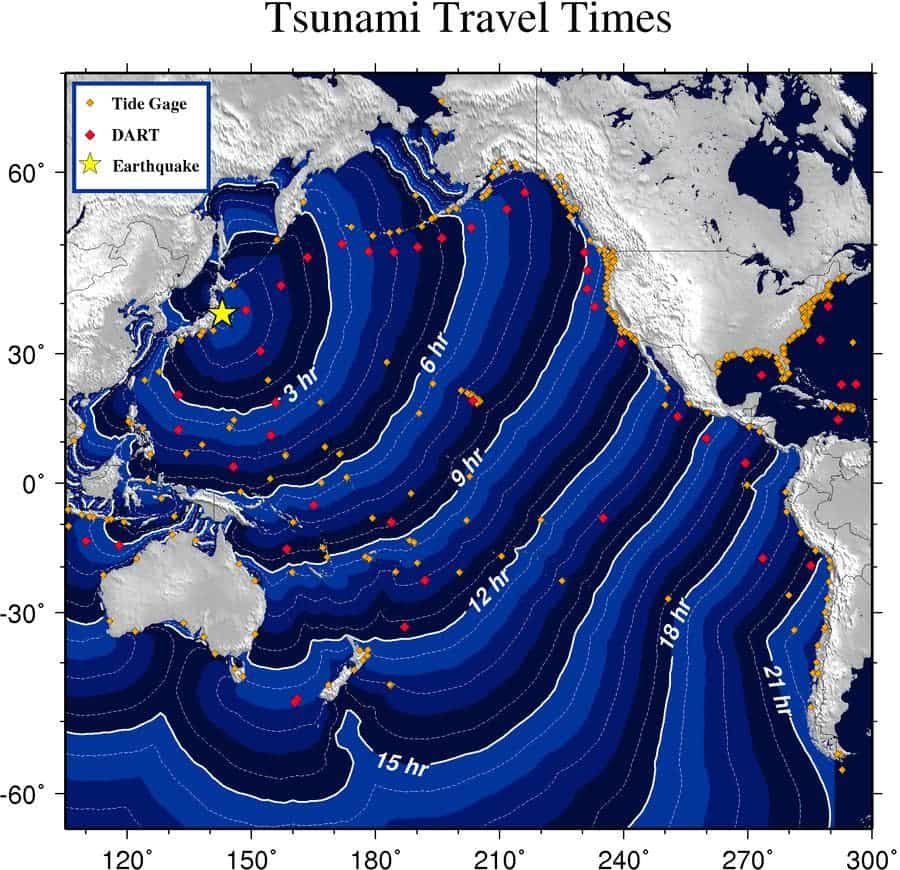
The thing is, temblors this big in the crust take place when a long, relatively straight fault line ruptures; a classical example for this would be Peru or Chile, but not Japan, because that tectonic plate boundary is not straight at all, but very irregular. According to USGS, an earthquake this big would require a huge rupture, of more than 300 miles. To top things off, this type of earthquake was perfect for tsunami generation, because it was very big, and at a very shallow depth.